January 21, 2026
Categories:
Secure Communication Without Personal Identifiers: Messenger Comparison
Article written with ChatGPT AI
A practical guide to secure messengers that create user identity without phone numbers or emails—and how modern architectures make this possible.
*Resume created with artificial intelligence
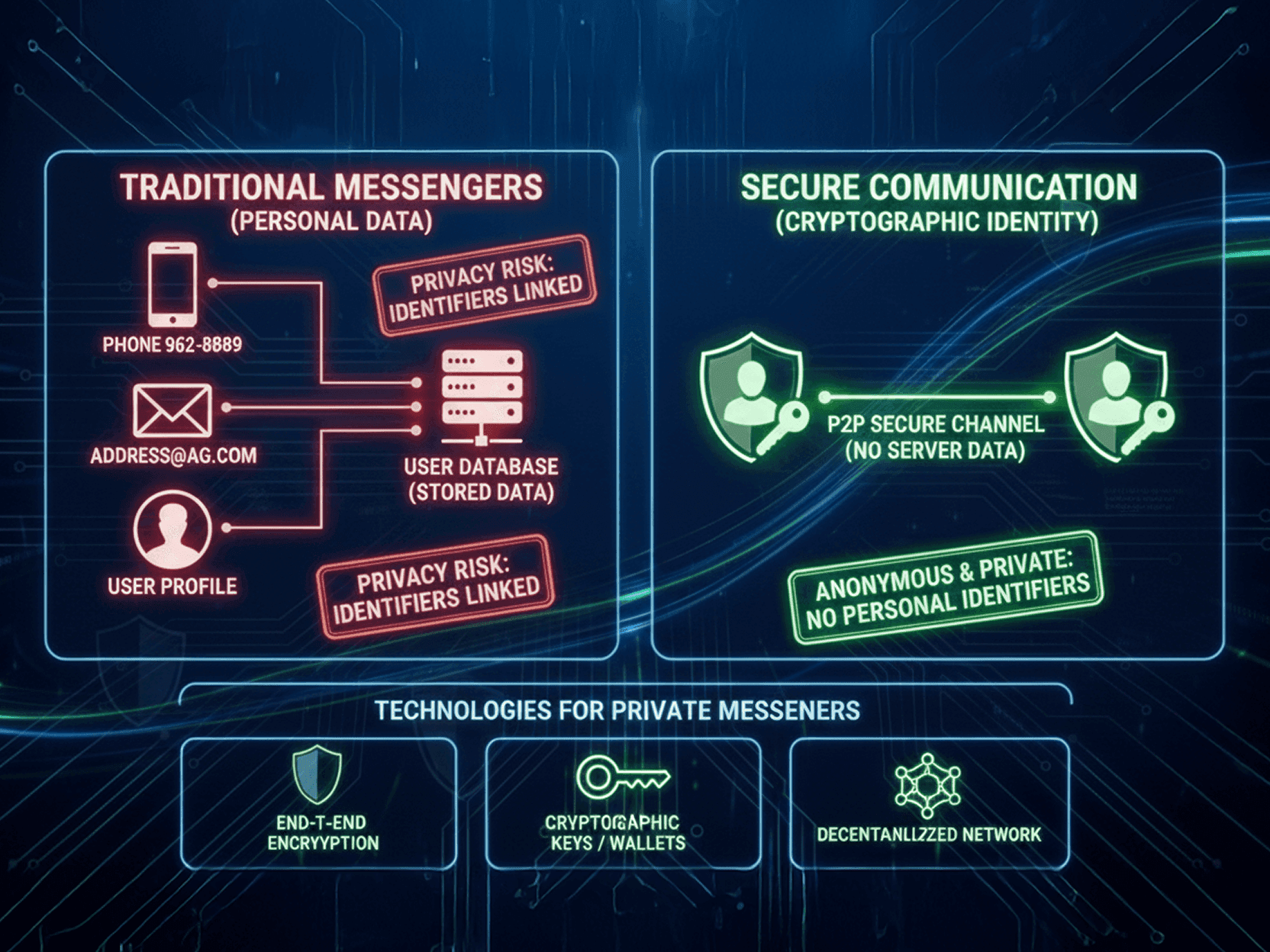
For years, messaging apps treated phone numbers and emails as harmless login tools. Today, we know better. These identifiers are routinely reused across platforms, leaked in breaches, scraped for profiling, and exploited for impersonation. Once tied to your chats, they quietly become a map of who you talk to, when, and how often.
The good news? Messaging architecture has evolved. Modern secure messengers can now create a user identity without collecting real-world identifiers at all. This shift reduces exposure to data leaks, minimizes metadata trails, and gives users genuine control over how they appear—and to whom. Privacy is no longer just a promise in a policy; it can be a property of the system itself.
The technology behind anonymous identity
To avoid phone numbers and emails, messengers rely on alternative identity models:
Cryptographic keys as identity. Instead of usernames tied to personal data, accounts are generated from public/private key pairs. The public key acts as an address; the private key proves ownership.
Decentralized or Web3-inspired models. Some apps borrow concepts from blockchain systems—self-generated keys, local custody, and user-controlled recovery phrases.
Peer-to-peer communication. Calls and messages can be routed directly between devices, reducing reliance on centralized identity services.
End-to-end asymmetric encryption. Messages are encrypted using the recipient’s public key, ensuring only the intended device can decrypt them.
The definitive list of private messengers
Not all messengers that avoid phone numbers or emails do so for the same reason—or with the same guarantees. Some focus on anonymity, others on decentralization, others on enterprise trust.
EXTRA SAFE
Main features:
Cryptographic identity generated on the device, encrypted 1-to-1 and group chats, device-to-device (P2P) voice and video calls, user-controlled recovery phrase.Benefits:
EXTRA SAFE is designed so identity exists independently of real-world identifiers. User profiles are based on cryptographic keys rather than accounts tied to contact data. Every call connects device-to-device (P2P) and is protected with blockchain algorithms, reducing exposure to intermediaries. EXTRA SAFE uses end-to-end asymmetric encryption to ensure only the intended devices can access message content.Payment model:
Free core communication features.
Session
Main features:
Key-based user IDs, asynchronous messaging, onion-routed message delivery through multiple nodes.Benefits:
Session emphasizes resistance to traffic analysis by separating message routing from user identity. Because accounts are generated locally, users can communicate without submitting phone numbers or emails. The architecture prioritizes metadata reduction, particularly in hostile network environments.Payment model:
Free.
SimpleX Chat
Main features:
Pairwise contact identifiers, no global user ID, optional server selection, end-to-end encryption.Benefits:
SimpleX Chat removes the concept of a public identity entirely. Each conversation uses a separate identifier, making it extremely difficult to correlate contacts or reconstruct social graphs. This approach is especially relevant for users concerned about long-term profiling.Payment model:
Free.
Threema
Main features:
Randomly generated user ID, contact verification via QR codes, enterprise management options.Benefits:
Threema offers a well-established privacy model that separates identity from personal data by default. It is frequently adopted by businesses and regulated organizations that require predictable security guarantees and formal compliance documentation.Payment model:
Paid app (one-time purchase).
Status
Main features:
Ethereum-based identity, integrated crypto wallet, decentralized community chats.Benefits:
Status is built around the concept of self-sovereign identity. User accounts are blockchain addresses controlled by private keys, aligning messaging with broader Web3 ecosystems. This model appeals to users already familiar with decentralized applications and wallet-based authentication.Payment model:
Free.
Comparison — how identity and data are handled
Aspect | EXTRA SAFE | Session | SimpleX Chat | Threema | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Account identity | Cryptographic key | Cryptographic key | Pairwise IDs | Random ID | Blockchain address |
Phone/email required | Not used | Not used | Not used | Optional | Not used |
Encryption model | End-to-end asymmetric encryption | End-to-end encryption | End-to-end encryption | End-to-end encryption | End-to-end encryption |
Call architecture | Device-to-device (P2P) | Limited | Limited | Centralized relay | Mixed |
Metadata exposure | Minimized by design | Reduced | Strongly reduced | Low | Depends on usage |
Recovery method | User-held recovery phrase | Key backup | Invite-based | ID backup | Wallet recovery |
Key takeaway
Secure messaging no longer requires trading privacy for convenience. By using cryptographic identity and modern architectures, users can communicate without exposing phone numbers or emails. EXTRA SAFE brings this together in a practical way: Every call connects device-to-device (P2P) and is protected with blockchain algorithms. EXTRA SAFE uses end-to-end asymmetric encryption.
If private communication is the goal, start with EXTRA SAFE and build your conversations on an identity you truly control.