February 4, 2026
6 Crypto Mistakes You Need to Avoid as a Beginner

Crypto adoption continues to grow each year, with millions of new users entering the ecosystem.
Some people come to crypto looking for new digital tools or more flexible ways to move value. Others arrive through recommendations, online trends, or simple curiosity. What many beginners discover early on is that crypto works differently from traditional apps and financial services, especially when it comes to access, recovery, and permissions.
Most early mistakes do not happen during trading. They happen during setup and everyday use. In crypto, these decisions often have permanent consequences, including lost access or irreversible transactions.
Below are six common mistakes beginners make, along with practical ways to avoid them.
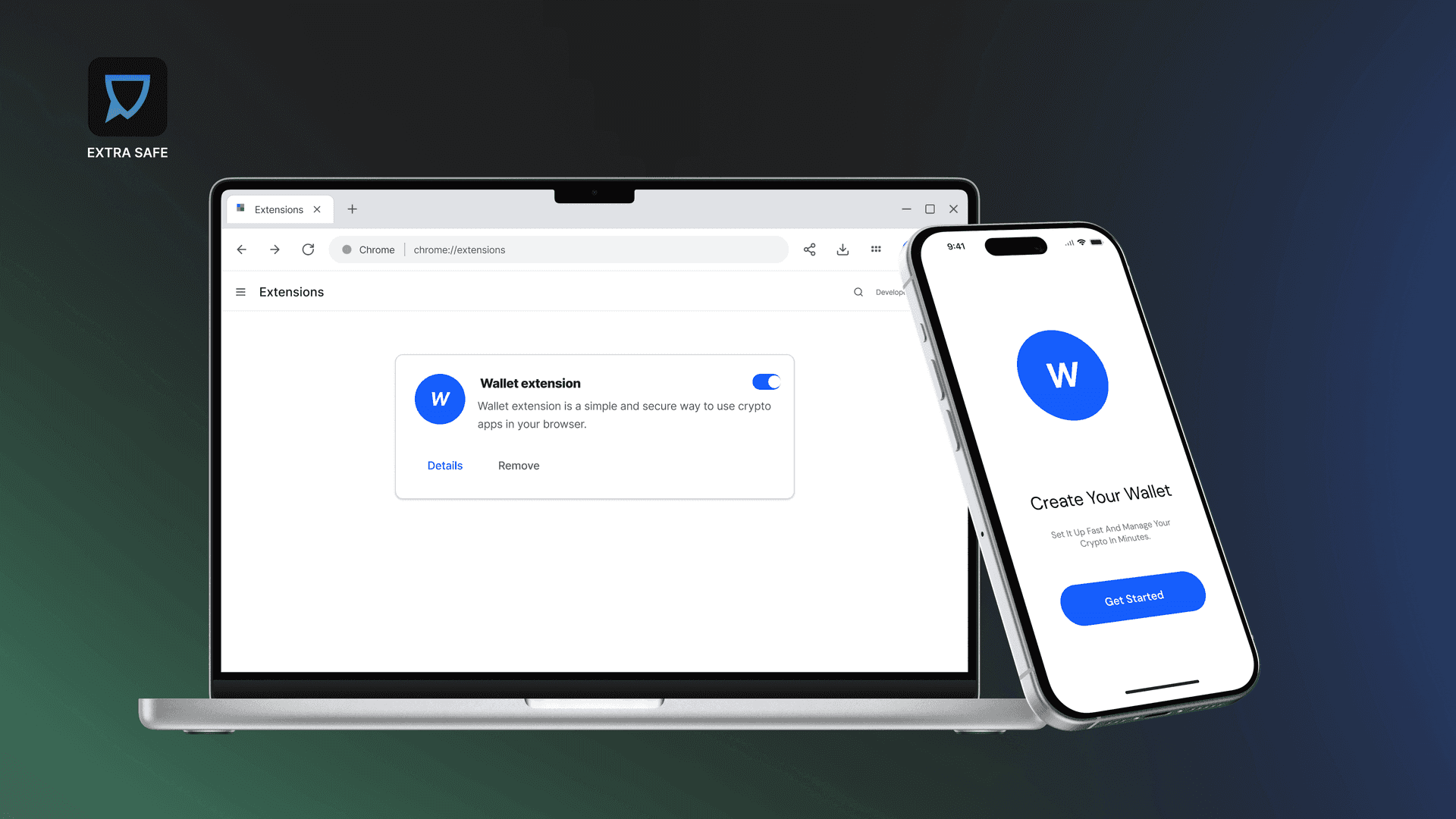
1. Installing a Fake Wallet or Browser Extension
Fake wallet apps and browser extensions frequently imitate real products. They copy names, logos, interfaces, and even user reviews, making them difficult to distinguish from legitimate tools at first glance.
These fakes are often discovered through ads, search results, or unofficial download links. Many users realize something is wrong only after wallet access or funds are compromised.
Wallets and extensions should always be downloaded from official websites or verified app stores. Before installing, the download link can be checked using VirusTotal.
To do this, open virustotal.com, select the URL tab, paste the link, and run a scan. VirusTotal checks the link against multiple security databases and reports whether it has been flagged as suspicious. Reviewing the developer name and publication history in the app store listing adds an additional layer of verification.
2. Ignoring the Seed Phrase During Wallet Setup
Crypto places responsibility directly on the user. Access is not managed through accounts, passwords, or customer support systems. Control begins at wallet creation.
That control is secured through the seed phrase. The seed phrase functions as the recovery mechanism for the wallet and reconnects the user to their assets if a device is lost or replaced.
When a wallet is created, the seed phrase appears as part of the setup process. How it is stored determines whether access can be restored later. Without the seed phrase, there is no recovery process, reset option, or override.
Treating this step as a formality often leads to permanent access issues. For a practical overview of storage methods and long-term handling, see our guide: How to Store a Seed Phrase to Secure Your Crypto.

3. Sending Funds to a Scam Address
Crypto transactions are sent to wallet addresses and cannot be reversed once confirmed. This makes address verification as important as the transaction itself.
Some giveaways, airdrops, or unofficial token pages ask users to send funds for “verification” or processing fees. Even when the site or message appears legitimate, the provided address may belong to an impersonator.
Before sending funds, paste the destination address into a blockchain explorer such as Etherscan and review the address page. Public reports, labels, or warnings often appear for addresses associated with scams or impersonation attempts. Every major blockchain has similar explorers that provide this visibility.
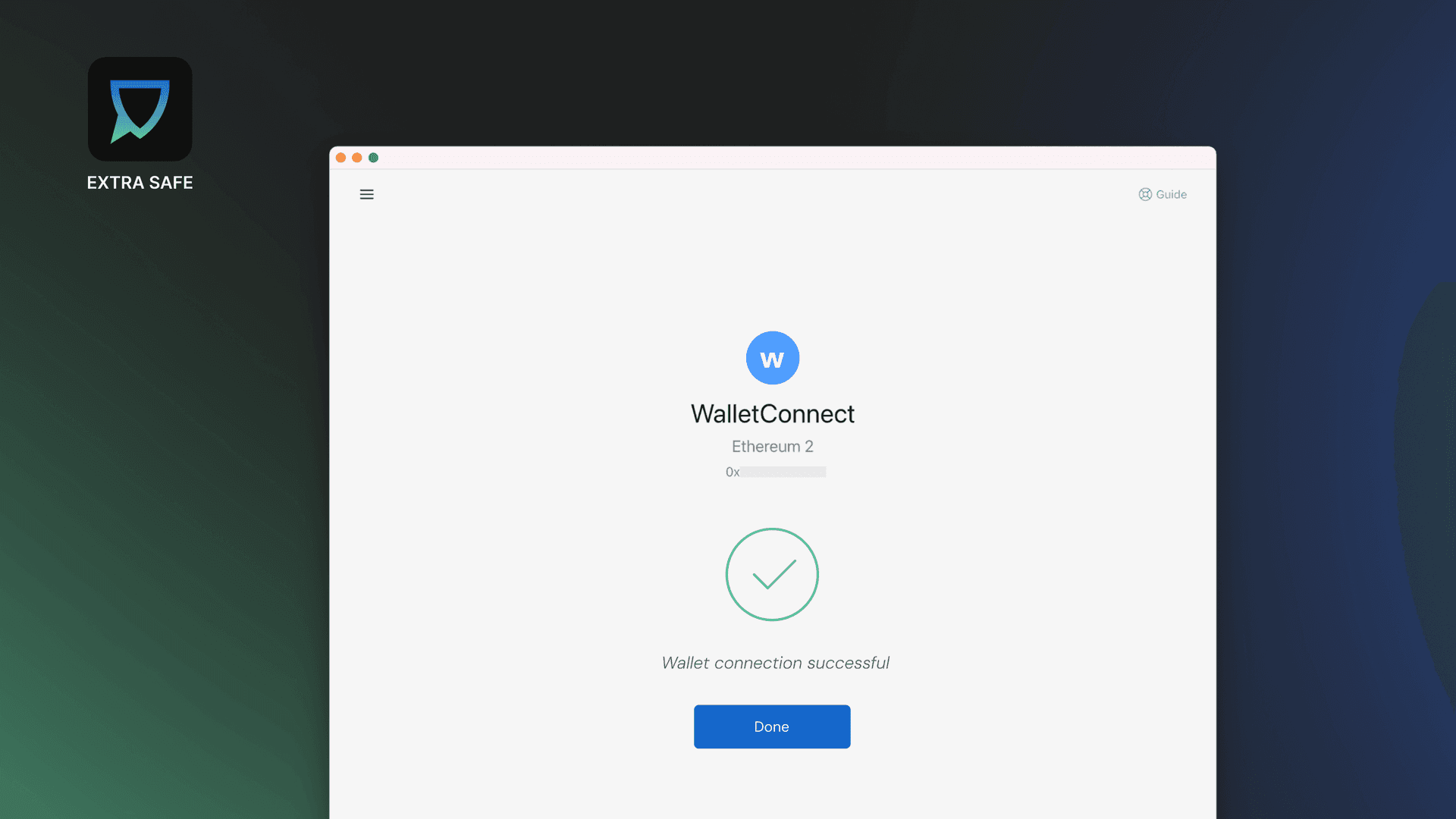
4. Connecting a Wallet Without Checking Permissions
Many crypto services require a wallet connection to function. This commonly happens on NFT platforms, DeFi tools, token dashboards, portfolio trackers, and airdrop pages.
When a site asks you to connect your wallet, it requests specific permissions. Some permissions allow balance viewing, while others enable contract interactions or transaction requests.
Before approving a connection, review what access is being requested and consider whether it is necessary for the action you are trying to complete. Unclear or unrelated requests are better skipped.
To receive alerts during risky wallet connections or signing requests, browser extensions such as Scam Sniffer can warn users during suspicious Web3 interactions.
5. Approving Token Access Without Reviewing Details
After connecting a wallet, some services request additional confirmation. This usually appears as a prompt to approve token access or sign a message.
Token approvals allow a smart contract to interact with a specific token on your behalf. These approvals are separate from transactions and often remain active for future use with the same contract.
Before approving access, review the details shown in the wallet confirmation window, including the token name and the contract requesting permission. Existing approvals can be reviewed on Etherscan, where active permissions and their scope are visible.
If the approval amount or the contract’s purpose is unclear, stopping and reviewing the request helps reduce unnecessary exposure.

6. Exposing Crypto Information Through Non-Encrypted Channels
Sharing wallet addresses or transaction details is sometimes necessary. When this information is exchanged through channels not designed for secure communication, it can be copied, stored, or resurfaced later.
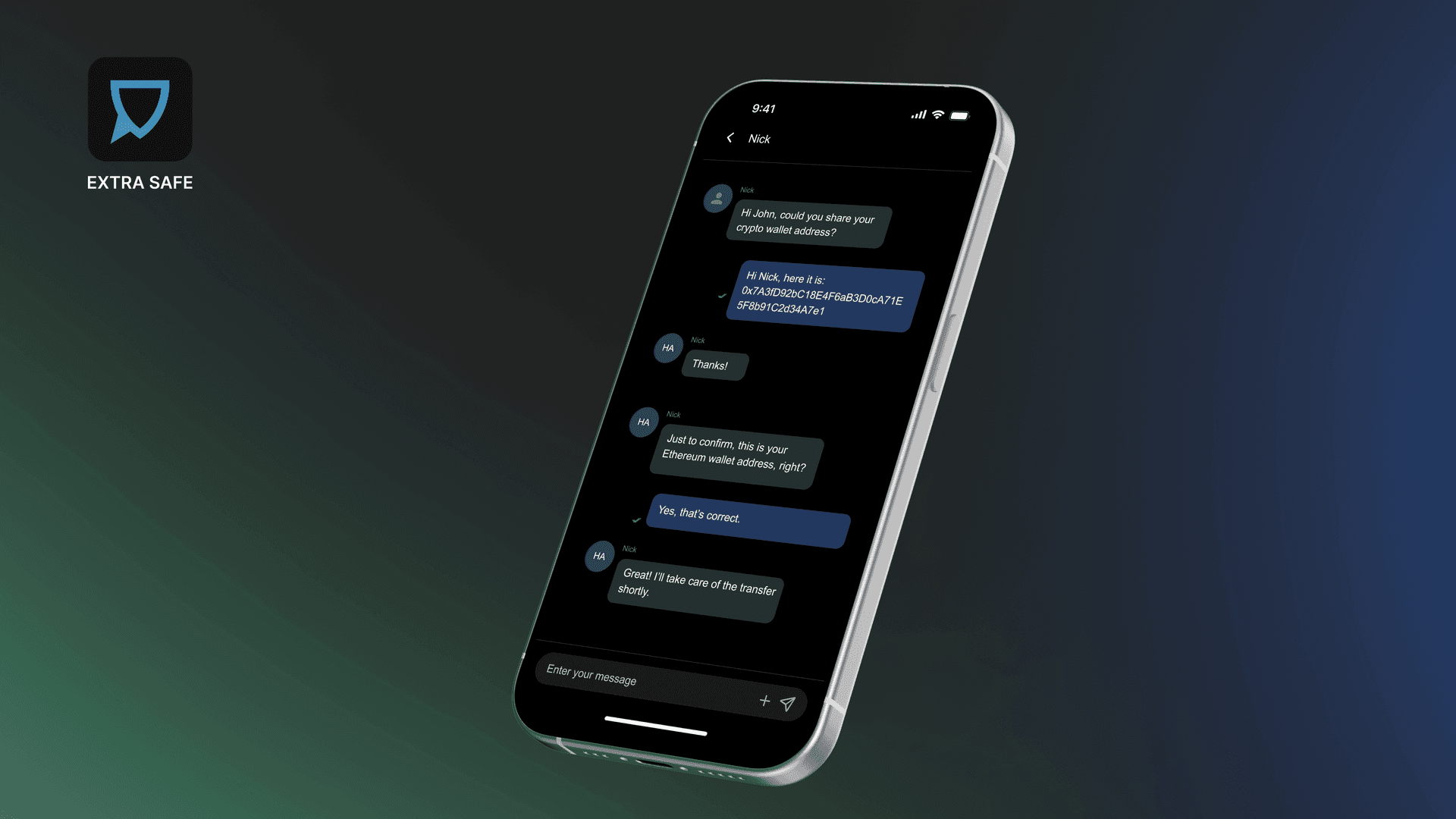
For this kind of exchange, use secure communication tools such as EXTRA SAFE Chat. It is built on crypto infrastructure and secures your messages, files, and images with end-to-end encryption, while cryptographic keys are created and kept on your devices.
Download EXTRA SAFE Chat on iOS and Android. Prefer a browser version? Visit extrasafe.chat